17 Dmarc Record Gmail Tips: Ultimate Security Setup Guide
Introduction to DMARC Record and Gmail Security

Setting up a secure email environment is crucial for protecting your personal or business communications from spam, phishing, and other malicious activities. One of the key components in achieving this security is the DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) record. When integrated with Gmail, DMARC significantly enhances the security of your email ecosystem. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore 17 tips for setting up a DMARC record with Gmail for an ultimate security setup.
Understanding DMARC and Its Importance

Before diving into the setup process, it’s essential to understand what DMARC is and why it’s vital for email security. DMARC is a protocol that helps prevent email spoofing by verifying the authenticity of the sender’s domain. It does this by checking the sender’s IP address against the domain’s SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) records. This ensures that only authorized senders can send emails on behalf of your domain, reducing the risk of phishing and spam.
Setting Up DMARC Record with Gmail

To set up a DMARC record with Gmail, follow these steps: - Step 1: Create a DMARC record. This involves generating a TXT record that includes your domain’s DMARC policy. The basic format of a DMARC record is:
<policy>; pct=<percentage>;
- Step 2: Publish the DMARC record in your domain’s DNS settings. This makes the record accessible to receiving email servers.
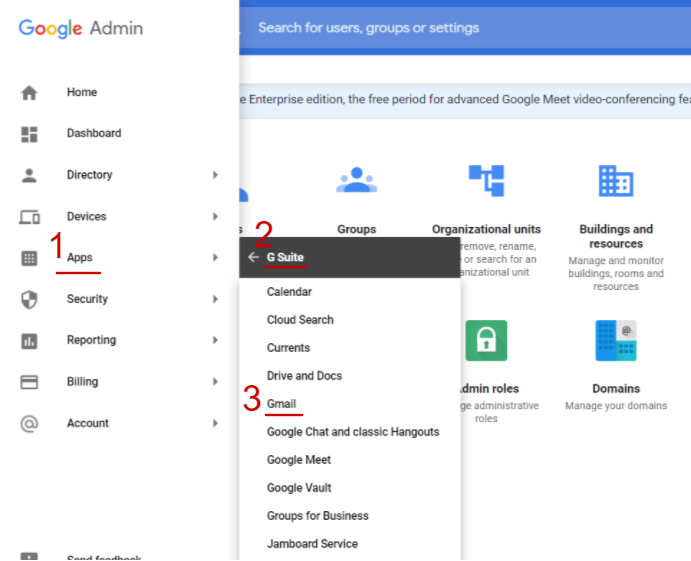
- Step 3: Configure Gmail to work with your DMARC record. This may involve setting up Gmail’s authentication features or adjusting your domain’s settings within the Google Admin Console.
17 Tips for Ultimate DMARC Record Gmail Security Setup

Here are 17 tips to help you set up and optimize your DMARC record for enhanced Gmail security: 1. Start with a Monitoring Policy: Begin with a monitoring policy (
p=none) to gather data on email senders without affecting delivery.
2. Implement SPF and DKIM: Ensure you have SPF and DKIM records set up, as DMARC relies on these for authentication.
3. Use a High Percentage: Gradually increase the percentage of emails that are subject to DMARC checks to minimize disruptions.
4. Set Up Reporting: Configure reporting to receive feedback on emails that fail DMARC checks, helping you identify and fix issues.
5. Monitor Your Domain’s Reputation: Keep an eye on your domain’s reputation, as DMARC can impact deliverability.
6. Educate Users: Inform your users about the importance of DMARC and how it affects email sending and receiving.
7. Test Thoroughly: Before enforcing a strict DMARC policy, test it extensively to avoid unintended blocking of legitimate emails.
8. Include Subdomains: Consider including subdomains in your DMARC policy to protect them from spoofing.
9. Stay Up-to-Date: Regularly review and update your DMARC record as your email infrastructure changes.
10. Use Aggregate Reports: Aggregate reports provide a summary of DMARC check results, helping you identify trends and issues.
11. Implement a Feedback Loop: Set up a feedback loop with your email service provider to receive complaint feedback, which can help in adjusting your DMARC policy.
12. Check for Alignment: Ensure that the domain in the “From” header aligns with the domain in the SPF or DKIM records.
13. Avoid Overly Strict Policies: Unless absolutely necessary, avoid starting with a strict policy (p=reject), as it can block legitimate emails.
14. Consider Third-Party Services: Utilize third-party services that can help in setting up, monitoring, and maintaining your DMARC records.
15. Integrate with Other Security Measures: Combine DMARC with other email security measures like two-factor authentication and encryption.
16. Regularly Review Reports: Regularly go through DMARC reports to identify potential issues and adjust your policy accordingly.
17. Be Patient: Setting up and optimizing DMARC can take time, so be patient and methodical in your approach.
Best Practices for Ongoing Management

Ongoing management of your DMARC record is crucial for maintaining its effectiveness. This includes: - Regularly Reviewing DMARC Reports: To identify and address potential issues. - Updating Your DMARC Policy: As needed, based on the insights gained from reports and changes in your email ecosystem. - Ensuring Alignment with SPF and DKIM: Regular checks to ensure these records are up-to-date and aligned with your DMARC policy.
| DMARC Policy | Description |
|---|---|
| p=none | Monitoring policy, does not affect email delivery. |
| p=quarantine | E-mails that fail DMARC are sent to spam. |
| p=reject | E-mails that fail DMARC are rejected. |

📝 Note: Always test your DMARC setup thoroughly before moving to a strict policy to avoid blocking legitimate emails.
In conclusion, setting up a DMARC record with Gmail is a critical step in securing your email communications. By following the 17 tips outlined in this guide and maintaining your DMARC record, you can significantly reduce the risk of email spoofing and phishing. Remember, email security is an ongoing process, and staying vigilant and informed is key to protecting your digital communications.
What is DMARC and how does it work?

+
DMARC is a protocol that helps prevent email spoofing by verifying the authenticity of the sender’s domain through SPF and DKIM checks.
Why is it important to set up a DMARC record with Gmail?

+
Setting up a DMARC record with Gmail enhances email security by preventing spoofing and reducing the risk of phishing and spam.
How do I start setting up a DMARC record for my domain?

+
Start by creating a TXT record with your DMARC policy and publishing it in your domain’s DNS settings. Then, configure Gmail to work with your DMARC record.



